Factors that Influence the Permeability Analysis in Magnetic Resonance Studies of the Prostate
Marcio Vieweger Vasques and Christina Rodrigues Gonçalves Vasques
DOI10.21767/2471-9943.100023
Fisico-Medico, SHLS 716 Set N, Block DF, 70390-901, Brazil
- Corresponding Author:
- Marcio Vieweger Vasques
Fisico-Medico, SHLS 716 Set N, Block DF, 70390-901, Brazil.
Tel: 6121915050
E-mail: m.vasques@clinicavillasboas.com.br
Received date: June 21, 2016; Accepted date: July 16, 2016; Published date: July 22, 2016
Citation: Vasques MV, Vasques CRG. Factors that Influence the Permeability Analysis in Magnetic Resonance Studies of the Prostate. Colorec Cancer 2016, 2:3.
Abstract
Methods: The permeability analysis was performed using the IntelliSpace portal, manufactured by PHILIPS with the Permeability package. The variables changed during processing were the AIF, temporal and spatial smoothing filters. For each equipment field strength a processing protocol was created informing the injection time, the relaxativity and the concentration of the contrast agent.
Results and Discussion: There is a significant difference in the values of permeability between the Manual and Automatic AIF processing. Temporal smoothing filters showed greater variation when using the medium setting. This variation occurs for all examined criteria (ktrans, kep, Ve and Vp). Spatial smoothing filters do not alter substantially the results of the permeability analysis.
Conclusion: There is a big difference in the result of permeability obtained comparing the Automatic and Manual AIF analysis, and may be in the order of 250%. Temporal and spatial smoothing filters have small, non-significant variations in the results.
Keywords
Prostate MRI; Multiparametric analysis; Prostate cancer; Prostate multiparametric; Permeability; Prostate permeability
Objetctive
The objective of this study is to demonstrate some possible results variations that occur in MRI permeability studies of the prostate, taking into account the post processing variables that can be adjusted by the operator on the IntelliSpace Portal, manufactured by PHILIPS Healthcare [1,2].
Materials and Methods
The permeability analysis was performed using the IntelliSpace portal, manufactured by PHILIPS Healthcare with the Permeability package. The variables changed during processing were the AIF (manual or disabled), temporal and spatial smoothing filters. For each equipment field strength a processing protocol was created informing the injection time, the relaxivity and the concentration of the contrast agent (Tables 1 and 2).
| 1.5T Magnetic Field Strength | |
|---|---|
| Contrast Relaxivity | 3.9 s-1.mmol-1 |
| Injection Dose | 0.2 mmol/kg |
| Injection Duration | <5 seconds (shortest) |
| Hematocrit | 45% |
Table 1: Preset for post-processing on 1.5T equipment.
| 3T Magnetic Field Strength | |
|---|---|
| Contrast Relaxivity | 3.9 s-1.mmol-1 |
| Injection Dose | 0.1 mmol/kg |
| Injection Duration | <5 seconds (shortest) |
| Hematocrit | 45% |
Table 2: Preset for post-processing on 3T equipment.
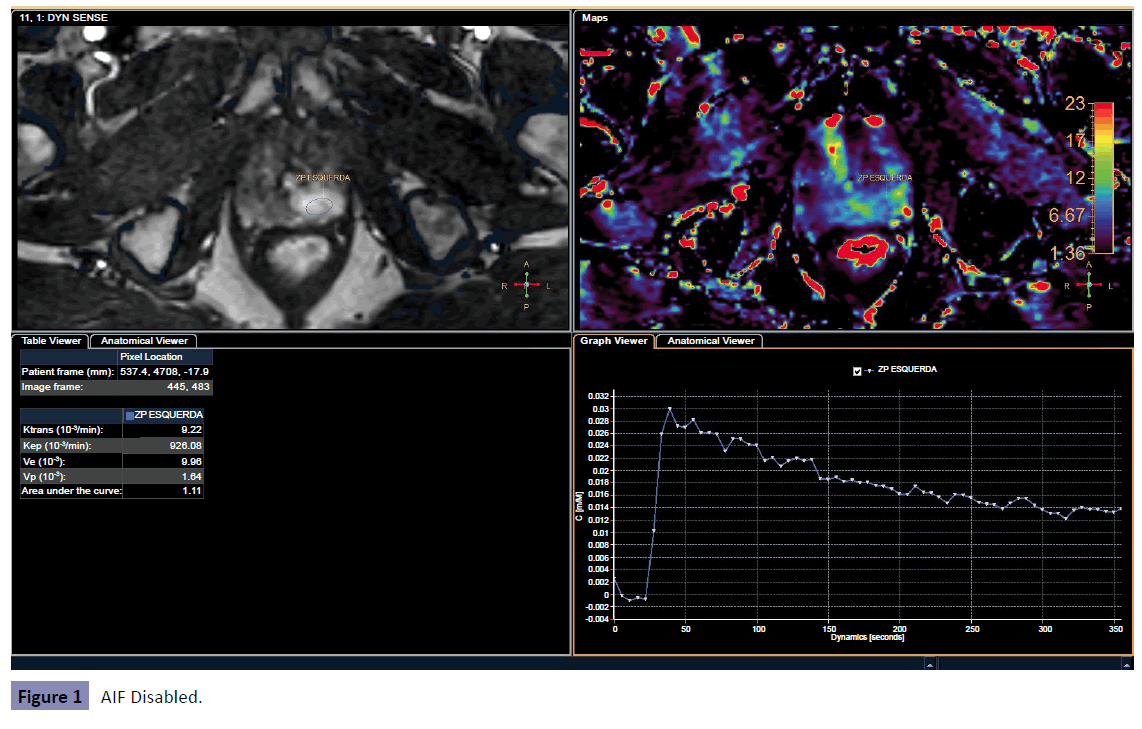
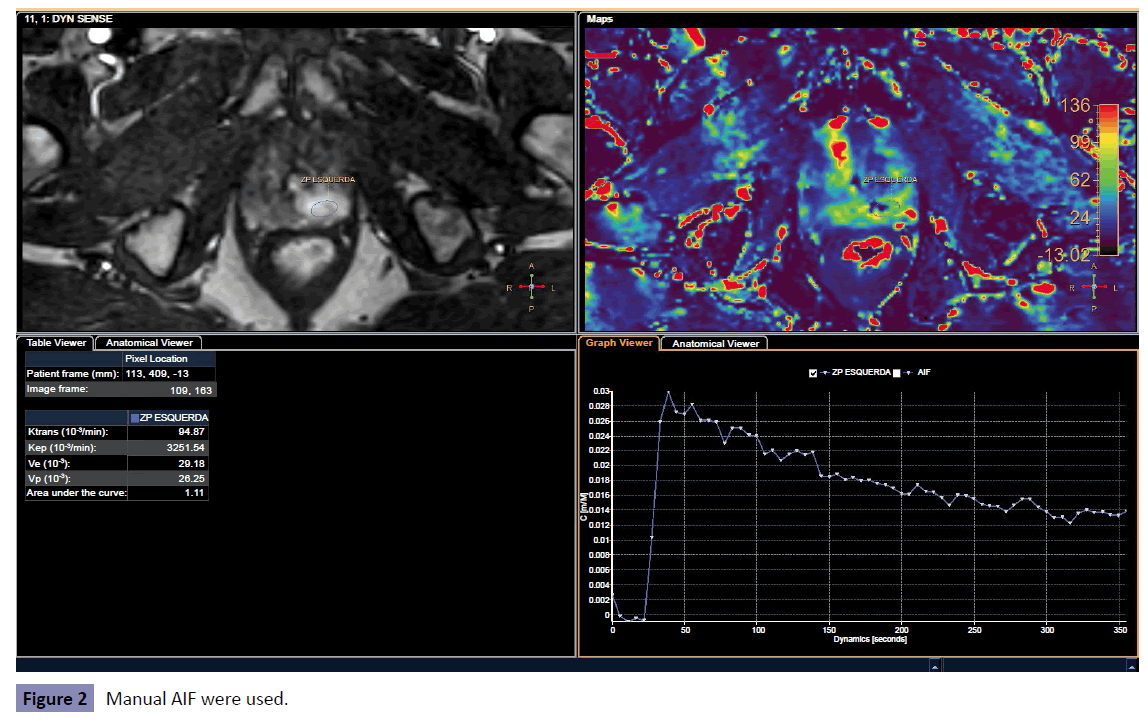
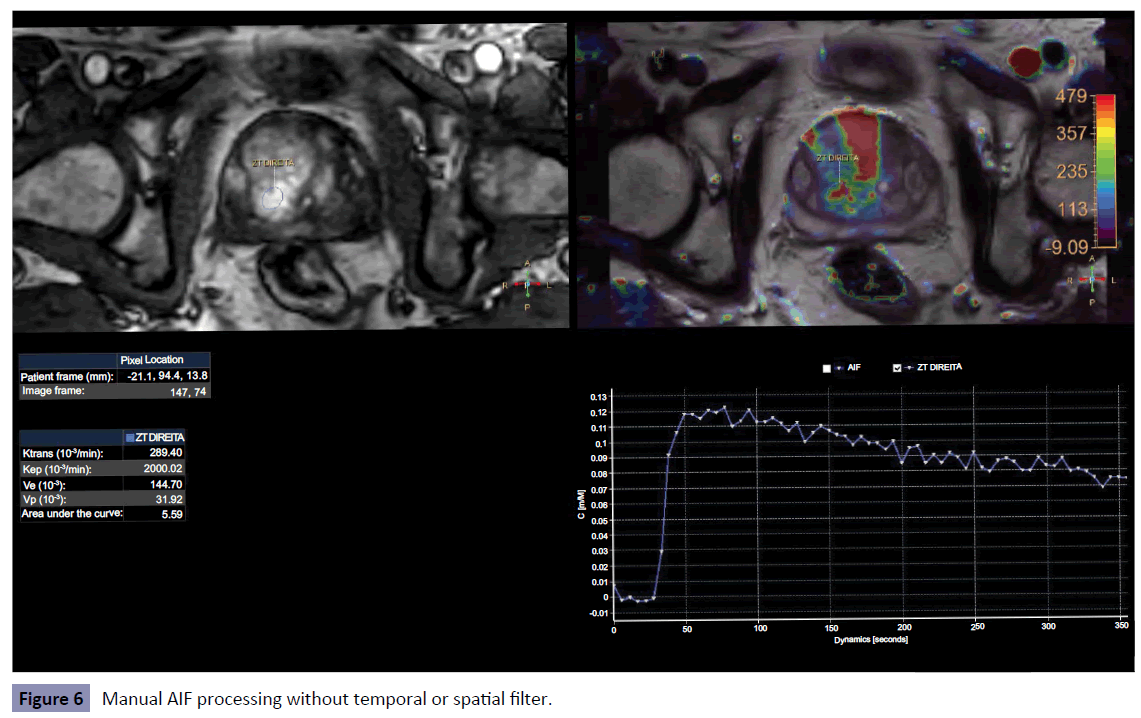
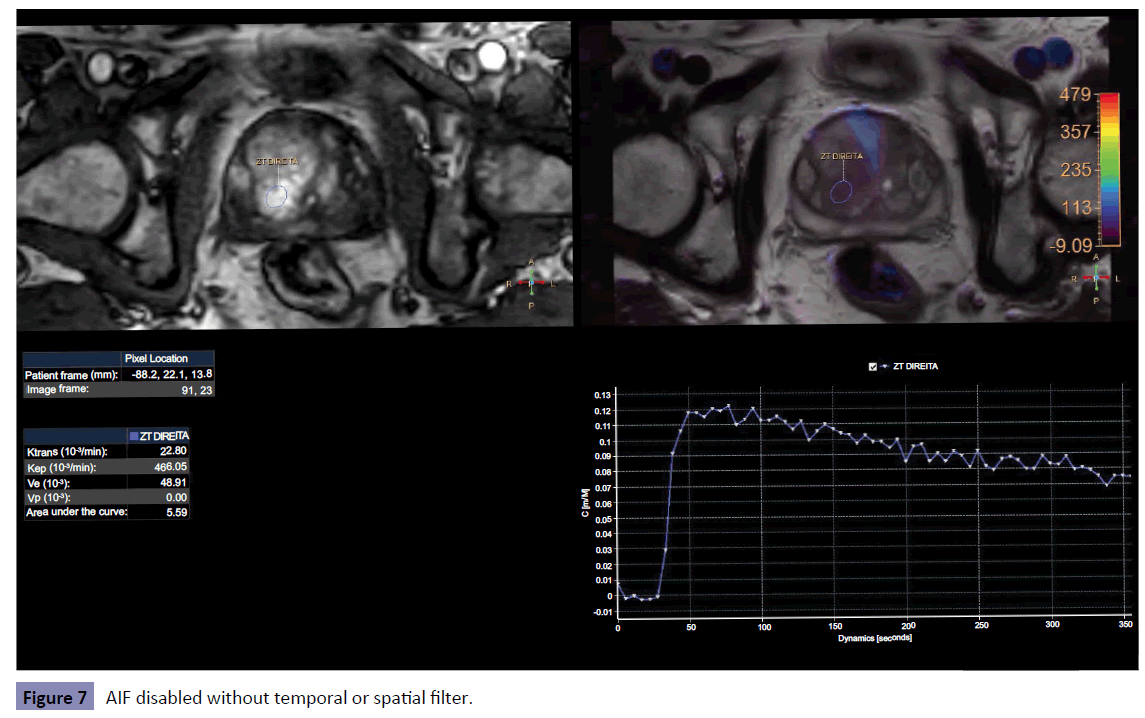
The spatial and temporal filters were altered for all four configurations (none, weak, medium, strong). For the manual AIF processing, the region of interest was positioned on the common iliac artery. The Figures show the results for both disabled and Manual AIF processing (no temporal or spatial filter were used) in a suspicious nodule (PIRADS V) in the left peripheral zone (Figures 1 and 2).
The permeability analysis was made using a dynamic sequence with high temporal resolution (approximately 5 seconds) and 65 dynamic phases. To obtain a T1 MAP of the prostate tissue the same sequence was acquired before the administrations of IV contrast with one dynamic and different flip angles of 5 and 15 degrees (Figures 3-5).
Results and Discussion
Thirty patients were submitted to prostate MRI for permeability analysis and the results obtained were:
• The difference, in percentage, between the manual AIF and the disabled AIF processing were (83.66 ± 19.82)% for ktrans (51.84 ± 10.95)% for kep, (68.86 ± 32.96)% for Ve and (91.99 ± 4.02)% for Vp
• The effective difference for ktrans processing using different temporal and spatial filters, compared with the result without any filter (Table 3).
| Temporal Smoothing | Weak | Medium | Strong | Spatial Smoothing | Weak | Medium | Strong |
| 9.86±28.34 | 13.64±25.06 | 5.93±21.74 | 1.07±24.54 | -0.10±44.44 | -9.33±49.25 |
Table 3: Effective difference for ktrans processing using different temporal and spatial filters.
• For the kep, the effective difference was (Table 4).
| Temporal Smoothing | Weak | Medium | Strong | Spatial Smoothing | Weak | Medium | Strong |
| -9.21 ± 213.57 | -5.65 ± 34.92 | -22.63 ± 236.48 | 11.01 ± 148.90 | -10.28 ± 221.21 | -75.02 ± 180.91 |
Table 4: For the kep, the effective difference.
• For the Ve, the effetctive difference was (Table 5).
| Temporal Smoothing | Weak | Medium | Strong | Spatial Smoothing | Weak | Medium | Strong |
| 18.74 ± 65.19 | 25.24 ± 61.47 | 20.53 ± 48.30 | 0.18 ± 8.69 | 0.26 ± 16.59 | -1.05 ± 20.67 |
Table 5: For the Ve, the effective difference.
• For Vp, the difference was (Table 6).
| Temporal Smoothing | Weak | Medium | Strong | Spatial Smoothing | Weak | Medium | Strong |
| -0.32 ± 1.53 | -2.12 ± 3.55 | -5.11 ± 9.06 | -2.75 ± 7.54 | -4.85 ± 3.74 | -5.34 ± 4.66 |
Table 6: For Vp, the difference.
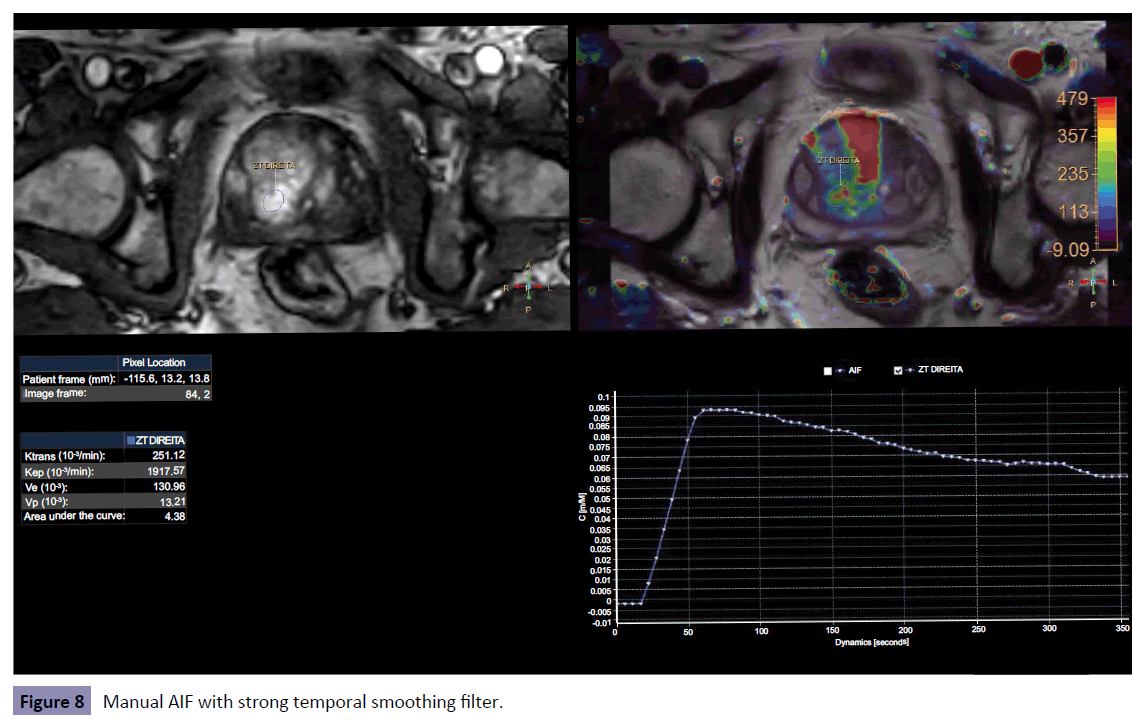
The Figures 6-8 shows some of these differences obtained after three different types of processing.
Discussion
• The use of temporal or spatial smoothing filters alters the results of all permeability parameters with differences superior than 100% [3].
• One of the greatest contribution for these variations is due to noise fluctuation of the dynamic acquisitions, more evident in equipments of higher filed strength.
• In general, the use of temporal and spatial smoothing filter doesn´t alter the behave of the perfusion curve (plateau), even with Manual or disabled AIF processing.
• Temporal smoothing filters presented a bigger variation in the results compared with spatial smoothing filters;
• There was a great difference between the results of manual AIF and disabled AIF processing [4-8].
Conclusions
The analysis concluded that there is a wide variation in the results of permeability using different post-processing techniques. Spatial smoothing filters do not exhibit so significant variations in the results compared to temporal smoothing filters. The difference in the obtained results with disabled and manual AIF are very considerable, which can lead to discrepant results for patients who are in active surveillance.
General Considerations
• The use of pulse sequences with CENTRA and Keyhole helps to minimize the noise fluctuation, allow to increase the spatial and temporal resolution on dynamic acquisitions.
• In general, even with more noise fluctuation, the image quality of 3T MRI equipment’s is better compared with 1.5T. The Signal-to-Noise Ratio is quite bigger, generating more detailed images, with better contrast and definition of tissues.
• For follow-up studies we recommend to use the same processing as the first exam, including filters and AIF region of interest positioning, minimizing possible results variations.
• The AUC (area under the curve) is exactly the same for both Manual and disabled AIF processing, so, it was not analyzed on this study.
• The study showed just the results variations of different sorts of processing on the permeability analysis and not the normal thresholds.
References
- Dickinson L, Ahmed HU, Allen C, Barentsz JO, Carey B, et al. (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging for the detection, localization and characterisation of prostate cancer: recommendations from a European consensus meeting. Eur Urol59:477-494.
- Hoeks CM, Barentsz JO, Hambrock T, Yakar D, Somford DM, et al. (2011) Prostate cancer: multiparametric MR imaging for detection, localization, and staging. Radiology261:46-66.
- Tofts OS, Brix G, Buckley DL, Evelhoch JL, HendersonE, et al. (1999)Estimating Kinetic Parameters From Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted MRI of a Diffusable Tracer: Standardized Quantities and Symbols.Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 10:223 232.
- Azahaf M, Haberley M, Betrouni N, Ernst O, Behal H, et al. (2015)Impact of Arterial Input Function Selection on the Accuracy of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Quantitative Analysis for the Diagnosis of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 43: 737-749.
- Mazaheri Y, Shukla-Dave A, Muellner A, Hricak H (2011)MRI of the Prostate: Clinical Relevance and Emerging Applications. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 33:258–274.
- Verma S, Turkbey B, Muradyan N, Rajesh A, Cornud F, et al. (2012)Overview of Dynamic Contrast- Enhanced MRI in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Management. AJR Am J Roentqenol198:1277–1288.
- Buckley DL, Roberts C, Parker GJM, Loque JP, Hutchinson CE (2004)Prostate Cancer: Evaluation of Vascular Characteristics with Dynamic Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR Imaging— Initial Experience. Radiology233:709–715.
- Visschere PJLD, Naesens L, Libbrecht L, Van Praet C, Lumen N, et al. (2016)What kind of prostate cancers do we miss on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging?. Eur Radiol26:1098–1107.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences